Compact Fourier Transform Spectrometer Simulation: GitHub
Purpose: We developed a Fourier transform spectrometer (FTS) to measure the spectrum of radiation sources between 50 GHz and 330 GHz, such as the cosmic microwave background. We have developed a ray-trace-based simulation with which we can model these recorded signal modification due to properties of the interferometer and the detection system.
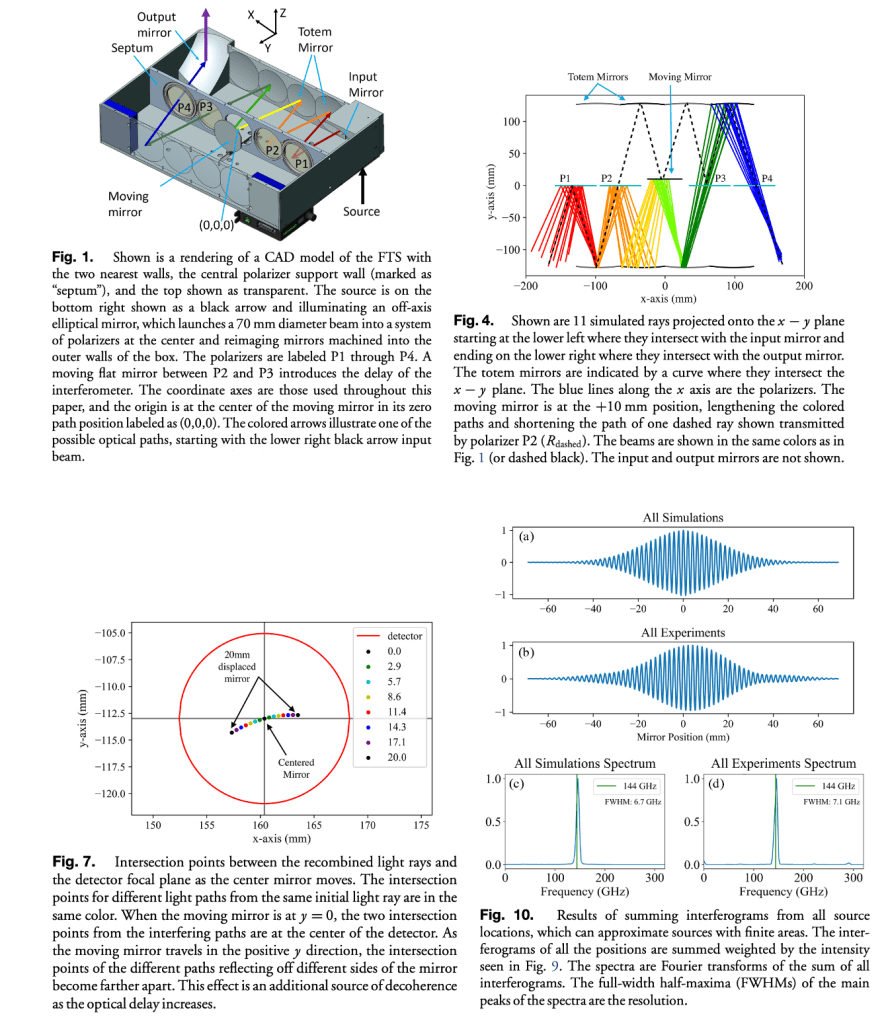
Methods and Materials: The optimization comprises parameters of the design, such as large étendu, maximal spectral resolution, compact size, operational simplicity, and light weight, that conflict and need to be balanced. The numerical simulation consists of two parts: time-stream signal analysis and a ray-trace-based simulation that includes polarization and path length calculations and can account for the effects of beam loss and change of focus as the delay-generating mirror travels on its path.
Results: The model was verified with measurements and used to understand the instrument’s systematic effects and to design new optimized configurations. It showed beam loss due to finite optical elements causing the modulating envelope, spatial and phase decoherence due to divergence and wide beam angle and source shifting.
Conclusions: The simulation can study the coherence level and frequency resolution of the FTS instrument. While not exercised in this study, the simulation also can be used to study the effect of mirror figure and polarizer non-idealities, walk-off rays in the beam due to the large étendu, as well as misalignment of optical elements.
Relevant publications
Z. Pan et al “Compact Millimeter-wavelength Fourier-Transform Spectrometer“. Applied Optics, 2019
MM Liu et al “Simulation and calibration of a compact millimeter-wavelength Fourier transform spectrometer“. Applied Optics, 2020